Current situation of the synthesis and use of geopolymers
Keywords:
geopolymers, aluminum-silicates, alkaline activation, technological intelligenceAbstract
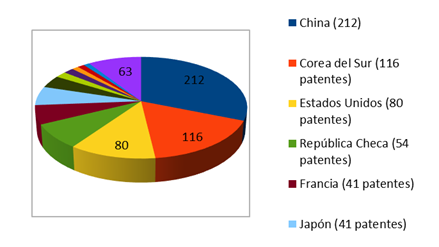
Cement is one of the most widely used building materials worldwide. For every ton produced, one ton of CO2 is emitted into the atmosphere, additionally, its production requires energy expenditure, implying the environmental effects of the mining activity. An eco-friendly alternative is represented by geopolymeric materials, which are inorganic polymeric matrices that can fulfill the binder function of cement, whose production minimizes the carbon damages. Geopolymers can be made using as precursors industrial residues rich in silicon and aluminum oxides, through an alkaline activation process, representing an alternative for the revaluation of many environmental liabilities, allowing the production of concretes of up to 50 Mpa of compressive strength. In the present investigation, a bibliometric and patentometric analysis of current trends in the use and synthesis of geopolymers was carried out, as well as the evolution of the technological process during the last 20 years. For this, a search equation was developed and later the Patent Inspiration platform was used for patent analysis and Thomson Reuters for scientific publications. It was found that the leading countries in patenting this technology are China, Korea and the United States. The present cartography of geopolymers makes it possible to publicize this technological innovation for the development of environmentally friendly construction materials which have not yet been widely investigated in Venezuela
Downloads
References
J. Davidovits, “Global Warming IMpact on the Cement and Aggregates Industries,” World Resour. Rev., vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 263–278, 1994
D. Hardjito, S. E. Wallah, Dody M. J. Sumajouw, and B. V. Rangan, “On the Development of Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete,” no. February, 2016
A. Neville, “Chloride Attack of Reinforcement Conccrete an Overview.Pdf,” Materials and Structures, vol. 28. pp. 63–70, 1995
J. Davidovits, “Properties of Geopolymer Cements,” First Int. Conf. Alkaline Cem. Concr., pp. 131–149, 1994
“Search and analyze patents - PatentInspiration.” [Online]. Available: http://www.patentinspiration.com/
“Home | Thomson Reuters.” [Online]. Available: https://www.thomsonreuters.com/en.html.
A. Mehta and R. Siddique, “An overview of geopolymers derived from industrial by-products,” Constr. Build. Mater., vol. 127, pp. 183–198, 2016
S. O. Sore, A. Messan, E. Prud’homme, G. Escadeillas, and F. Tsobnang, “Synthesis and characterization of geopolymer binders based on local materials from Burkina Faso – Metakaolin and rice husk ash,” Constr. Build. Mater., vol. 124, pp. 301–311, 2016
E. Nimwinya et al., “A Sustainable Calcined Water Treatment Sludge and Rice Husk Ash Geopolymer,” J. Clean. Prod., 2016
J. G. S. Van Jaarsveld, J. S. J. Van Deventer, and L. Lorenzen, “The potential use of geopolymeric materials to immobilise toxic metals: Part I. Theory and applications,” Miner. Eng., vol. 10, no. 7, pp. 659–669, 1997
S. Lee, A. van Riessen, C. M. Chon, N. H. Kang, H. T. Jou, and Y. J. Kim, “IMpact of activator type on the immobilisation of lead in fly ash-based geopolymer,” J. Hazard. Mater., vol. 305, pp. 59–66, 2016
H. W. Nugteren, M. B. Ogundiran, G. Witkamp, and M. T. Kreutzer, “Coal fly ash activated by waste sodium aluminate solutions as an immobilizer for hazardous waste,” 2011 World Coal Ash Conf., pp. 1–10, 2011
D. C. Comrie, J. H. Paterson, and D. J. Ritcey, “Applications of Geopolymer Technology to Waste Stabilization,” Third Int. Conf. New Front. Hazard. Waste Manag. Proc., p. 161–165r604, 1989
L. Zheng, W. Wang, and Y. Shi, “The effects of alkaline dosage and Si/Al ratio on the immobilization of heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash-based geopolymer,” Chemosphere, vol. 79, no. 6, pp. 665–671, 2010
Z. Yunsheng, S. Wei, C. Qianli, and C. Lin, “Synthesis and heavy metal immobilization behaviors of slag based geopolymer,” J. Hazard. Mater., vol. 143, no. 1–2, pp. 206–213, 2007
A. D. Cozzi, C. J. Bannochie, P. R. Burket, C. L. Crawford, and C. M. Jantzen, “Immobilization of radioactive waste in fly ash based geopolymers,” 2011 World Coal Ash Conf. – May 9-12, 2011 Denver, CO, USA, 2011
J. Temuujin et al., “Utilization of radioactive high-calcium Mongolian flyash for the preparation of alkali-activated geopolymers for safe use as construction materials,” Ceram. Int., vol. 40, no. PB, pp. 16475–16483, 2014
R. A. A. Boca Santa, C. Soares, and H. G. Riella, “Geopolymers with a high percentage of bottom ash for solidification/immobilization of different toxic metals,” J. Hazard. Mater., vol. 318, pp. 145–153, 2016
Q. Li et al., “Immobilization of simulated radionuclide 133Cs+by fly ash-based geopolymer,” J. Hazard. Mater., vol. 262, pp. 325–331, 2013
P. Sazama, O. Bortnovsky, J. Dědeček, Z. Tvaržková, and Z. Sobalík, “Geopolymer based catalysts-New group of catalytic materials,” Catal. Today, vol. 164, no. 1, pp. 92–99, 2011
S. Candamano, P. Frontera, A. Macario, F. Crea, J. B. Nagy, and P. L. Antonucci, “Preparation and characterization of active Ni-supported catalyst for syngas production,” Chem. Eng. Res. Des., vol. 96, pp. 78–86, 2015
S. Sharma, D. Medpelli, S. Chen, and D. K. Seo, “Calcium-modified hierarchically porous aluminosilicate geopolymer as a highly efficient regenerable catalyst for biodiesel production,” RSC Adv., vol. 5, no. 80, pp. 65454–65461, 2015
R. M. Novais, L. H. Buruberri, M. P. Seabra, and J. A. Labrincha, “Novel porous fly-ash containing geopolymer monoliths for lead adsorption from wastewaters,” J. Hazard. Mater., vol. 318, pp. 631–640, 2016
T. Luukkonen et al., “Removal of ammonium from municipal wastewater with powdered and granulated metakaolin geopolymer,” Environ. Technol. (United Kingdom), vol. 39, no. 4, pp. 414–423, 2018
Y. Ge, Y. Yuan, K. Wang, Y. He, and X. Cui, “Preparation of geopolymer-based inorganic membrane for removing Ni2+from wastewater,” J. Hazard. Mater., vol. 299, pp. 711–718, 2015
M. Naghsh and K. Shams, “Synthesis of a kaolin-based geopolymer using a novel fusion method and its application in effective water softening,” Appl. Clay Sci., vol. 146, no. March, pp. 238–245, 2017
Y. Zhang and L. Liu, “Fly ash-based geopolymer as a novel photocatalyst for degradation of dye from wastewater,” Particuology, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 353–358, 2013
E. Jämstorp, J. Forsgren, S. Bredenberg, H. Engqvist, and M. Strømme, “Mechanically strong geopolymers offer new possibilities in treatment of chronic pain,” J. Control. Release, vol. 146, no. 3, pp. 370–377, 2010
J. Forsgren, C. Pedersen, M. Strømme, and H. Engqvist, “Synthetic geopolymers for controlled delivery of oxycodone: Adjustable and nanostructured porosity enables tunable and sustained drug release,” PLoS One, vol. 6, no. 3, 2011
B. Cai, H. Engqvist, and S. Bredenberg, “Evaluation of the resistance of a geopolymer-based drug delivery system to tampering,” Int. J. Pharm., vol. 465, no. 1–2, pp. 169–174, 2014
“Geopolymer Institute – Promoting the geopolymer science since 1979.” [Online]. Available: https://www.geopolymer.org/
“Wagners.” [Online]. Available: https://www.wagner.com.au/
“Advance Concrete and Cement - Geopolymer Solutions.” [Online]. Available: http://www.geopolymertech.com/
“VOSviewer - Visualizing scientific landscapes.” [Online]. Available: http://www.vosviewer.com/
P. Duxson, A. Fernández-Jiménez, J. L. Provis, G. C. Lukey, A. Palomo, and J. S. J. Van Deventer, “Geopolymer technology: The current state of the art,” J. Mater. Sci., vol. 42, no. 9, pp. 2917–2933, 2007
A. Palomo, M. W. Grutzeck, and M. T. Blanco, “Alkali-activated fly ashes: A cement for the future,” Cem. Concr. Res., vol. 29, no. 8, pp. 1323–1329, 1999
H. Xu and J. S. J. Van Deventer, “The geopolymerisation of alumino-silicate minerals,” Int. J. Miner. Process., vol. 59, no. 3, pp. 247–266, 2000
P. Duxson, J. L. Provis, G. C. Lukey, S. W. Mallicoat, W. M. Kriven, and J. S. J. Van Deventer, “Understanding the relationship between geopolymer composition, microstructure and mechanical properties,” Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp., vol. 269, no. 1–3, pp. 47–58, 2005
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The opinions expressed by the authors do not necessarily reflect the position of the editor of the publication or UCLA. The total or partial reproduction of the texts published here is authorized, provided that the complete source and electronic address of this journal is cited. Authors have the right to use their articles for any purpose as long as it is done nonprofit. The authors can post on the internet or any other media the final approved version of their work.






.png)




