Evaluation of the physical and mechanical properties of bricks made with waste sludge from drinking water and wastewater treatment plants
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51372/gacetatecnica261.2Keywords:
structural materials, strength of materials, wastewater sludge, materials testingAbstract
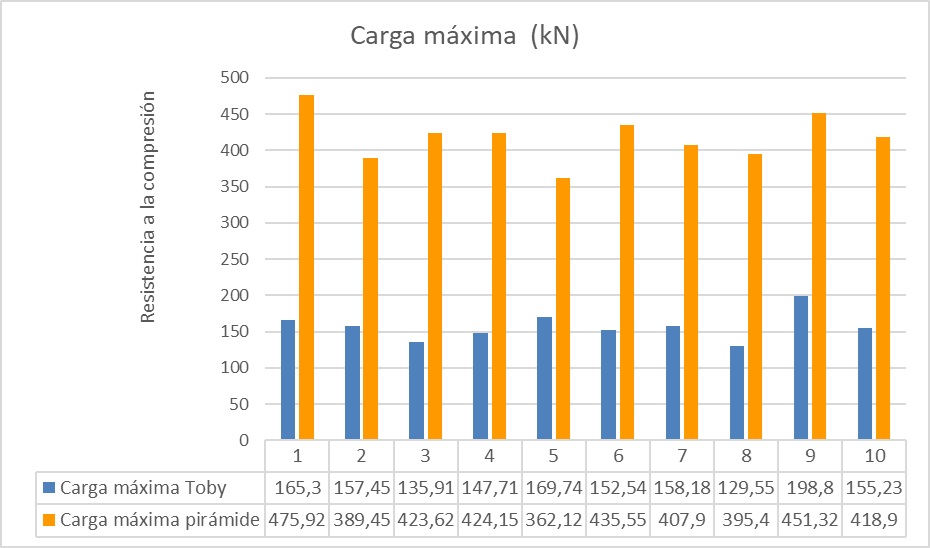
The objective of this research was to evaluate the physical and mechanical properties of bricks using waste sludge from drinking water treatment plants and wastewater treatment plants. For this purpose, an experimental and comparative study was carried out where 20 bricks made with 50% waste sludge were selected as a sample, they were compared with 20 traditional bricks (Pyramid 18H). According to the results, it has been identified that the compressive strength in traditional bricks corresponds to 14,73 MPa; being within type IV and type V; meanwhile, the resistance in bricks with mud (Toby) is 7,11 MPa, the same as those considered in type I and II bricks
Downloads
References
S. P. Muñoz-Pérez, F. Mimbela-Orderique, y E. D. Rodriguez-Lafitte, “Uso de ladrillos triturados en concreto: una revisión literaria,” Rev. Politécnica, vol. 17, no. 34, pp. 82–100, 2021, doi: 10.33571/rpolitec.v17n34a6, 2021
N. Serres, S. Braymand, y F. Feugeas, “Environmental evaluation of concrete made from recycled concrete aggregate implementing life cycle assessment,” J. Build. Eng., vol. 5, pp. 24–33, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2015.11.004, 2016
N. Roz-Ud-Din y S. Parviz, “Strength and durability of recycled aggregate concrete containing milled glass as partial replacement for cement,” Constr. Build. Mater., vol. 29, 2012, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.10.061, 2012
R. Global forum capacity building, “Developing capacities in times of COVID-19,” 2021. Disponible en: https://www.oecd.org/tax/transparency/documents/capacity-building-report-2021.htm, 2021
I. Andersen, “Programa de las Naciones Unidas para el Medio Ambiente,” UNEP, 2020. https://unsdg.un.org/sites/default/files/2020-07/UNEP_Working-with-the-environment-to-protect-people.pdf, 2020
M. Vargas Camareno y M. Montero Villalobos, “Estudio del uso del lodo residual de la empresa Extralum S. A. como material alternativo en la fabricación de cementos especiales,” Tecnol. en Marcha, vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 17–26, 2006
J. Espinoza and E. Santos, “Innovación en la gestión de lodos generados en plantas de tratamiento de aguas residuales de origen doméstico en Lima-Perú,” Rev. del Inst. Investig. la Fac. minas, Metal. y ciencias geográficas, vol. 24, no. 48, pp. 205–215, 2021, doi: 10.15381/iigeo.v24i48.21773, 2021
INEI, “Producción de agua potable en Lima Metropolitana disminuyó en 6.8%,” 2021. https://m.inei.gob.pe/prensa/noticias/produccion-de-agua-potable-en-lima-metropolitana-disminuyo-en-68-12804/, 2021
D. Zawal y A. M. Grabiec, “Influence of selected mineral additives on properties of recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) considering eco-efficiency coefficients,” Case Stud. Constr. Mater., vol. 17, no. September 2021, p. e01405, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01405, 2021
H. Ahmed, M. Tiznobaik, S. Huda, M. Islam, y M. Alam, “Recycled aggregate concrete from large-scale production to sustainable field application,” Constr. Build. Mater., vol. 262, p. 119979, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119979, 2020
M. Souad, D. Messaouda, y N. Ammar, “The potential of sludge from wastewater treatment plants to improve the mechanical properties of bricks,” J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag., vol. 25, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-023-01752-2, 2023
A. Bubalo, D. Vouk, L. Ćurković, M. Rogošić, D. Nakić, y C. Cheeseman, “Influence of combustion temperature on the performance of sewage sludge ash as a supplementary material in manufacturing bricks,” Constr. Build. Mater., vol. 404, no. August, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.133126, 2023
H. Gao, K. Zhou, D. Su, B. Zhang, and F. Cheng, “Sludge-based baking-free brick prepared by sewage sludge with high moisture content: Influence of process parameters and environmental risk assessment,” J. Environ. Chem. Eng., vol. 10, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2022.108576.
N. T. Minh Trang, N. A. Dao Ho, y S. Babel, “Reuse of waste sludge from water treatment plants and fly ash for manufacturing of adobe bricks,” Chemosphere, vol. 284, no. June, p. 131367, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131367, 2021
J. Mora and Z. Mariscal, “Correlación entre la satisfacción laboral y desempeño laboral,” Rev. dilemas Contemp. Educ. política y valores, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 148–162, 2019, Disponible en: https://www.dilemascontemporaneoseducacionpoliticayvalores.com/
index.php/dilemas/article/view/1307/123, 2019
M. Al-hashem et al., “Predicting the compressive strength of concrete containing,” Materials (Basel)., vol. 15, no. November, 2022, doi: 10.3390/ ma15217713, 2022
N. Cangussu, L. Silva, y L. Maia, “Incorporation of the Sludge of Sewage Treatment Plant on Ceramic Bricks Manufacture: An Exploratory Study,” U.Porto J. Eng., vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 10–19, 2022, doi: 10.24840/2183-6493_008.002_0002, 2022
J. D. dos S. S. Silva, R. L. Lopes, D. M. Torres, y R. D. R. da Silva, “Uso do lodo de ETE na produção de tijolos cerâmicos: Uma revisão sistemática de literatura,” Res. Soc. Dev., vol. 10, no. 8, p. e22010817200, 2021, doi: 10.33448/rsd-v10i8.17200, 2021
A. H. Noruzman, N. Palil, R. Ahmad, y K. S. Baharudin, “Application of waste treatment sludge from water treatment in brick production,” Int. J. Technol. Innov. Humanit., vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 33–40, 2020, doi: 10.29210/881101, 2020
L. Araujo, S. Molina, y L. Noguera, “Aprovechamiento de los lodos provenientes de plantas de tratamiento de aguas residuales como materia prima en la industria de la construcción: Revisión bibliográfica,” Rev. Agunkuyáa, vol. 1, pp. 21–28, 2018
C. Salazar et al., “Uso de lodos generados en los decantadores de una planta de tratamiento de agua potable como materia prima para la elaboración de ladrillos de construcción,” Trabajo de grado, Universidad Nacional de San Agustín, Perú, 2014
V. B. Gutiérrez Gonzales, “Tutoría académica y formación científica en estudiantes universitarios de Economía de la Universidad Nacional ‘San Cristóbal de Huamanga’-Perú, 2016,” Universidad Nacional de Educación Enrique Guzmán y Valle, 2017
F. Sandoval, A. del Cid,y R. Méndez, "Investigacion Fundamentos Y Metodologia", 2da Edición, Pearson Educación de México, México, 2011
I. M. Baas Chable, M. G. Barceló Méndez, y G. R. de Fátima Herrera Garnica, Metodología De La Investigación. 2012
M. P. Cachago, C. D. Caguano, y L. P. Viera, "Utilización De Lodos De La Planta De Tratamiento De Agua Residual De La Empresa Franz Viegener F.V.-Área Andina S.a. Para La Elaboración De Ladrillos Artesanales" Disponible en: http://www.dspace.uce.edu.ec/handle/25000/6928, 2016
D. Parra, “Diseño de sistema automatizado para el aprovechamiento de lodos residuales en PTAR y PTAP de Veolia Tunja,” Disponible en: http://repositorio.uan.edu.co/bitstream/123456789/8491/1/2023_ DavidSantiagoParra
Cubides.pdf, 2023
L. Rincón, “Aprovechamiento de los lodos de planta de tratamiento de aguas residuales en empresa Láctea, Municipio de Cogua,” (Monografía), Fundación Universidad de América, Recuperado de: http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11839/7455, 2019
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The opinions expressed by the authors do not necessarily reflect the position of the editor of the publication or UCLA. The total or partial reproduction of the texts published here is authorized, provided that the complete source and electronic address of this journal is cited. Authors have the right to use their articles for any purpose as long as it is done nonprofit. The authors can post on the internet or any other media the final approved version of their work.






.png)




