Behavior of the physical and mechanical properties of the concrete incorporating reed fiber into the mixture
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51372/gacetatecnica261.8Keywords:
reed fiber, CBR, dry density, sustainable concrete, durability of materialsAbstract
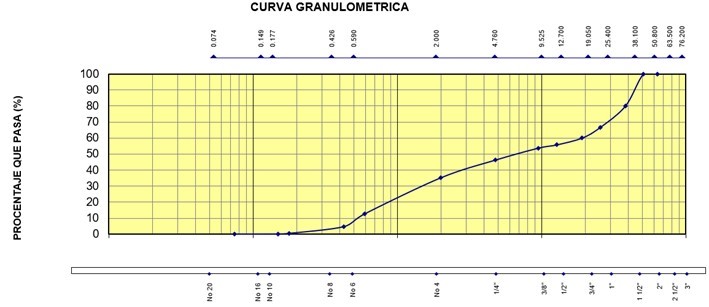
The objective of this study was to evaluate the behavior of the physical and mechanical properties of concrete by incorporating reed fiber into the mixture. For this purpose, it was proposed to add cane fiber to the dosage to analyze how this natural material modifies the concrete properties; Taking into account the possibility and openness of having alternative materials, an information search was carried out to analyze all the knowledge and information on the physical-mechanical properties, the latter validated by the California Bearing Ratio (CBR) that are presented in the different dosages of 0,0%; 0,8%; 1,2% and 1,6% reed fiber. As a result, it was obtained that the concrete pattern had a maximum dry density of 2,06 gr/cm³, an optimal moisture content of 3,43% and a CBR of 92% at a Penetration of 0,2” at 100% maximum dry density, and a CBR at 82% in a Penetration of 02” at 95% of maximum dry density. However, with the dosage of reed fiber of 0,8%, the results were a maximum dry density of 2,07gr/cm³, an optimal moisture content of 3,09% and a CBR of 97,8% in a Penetration of 0,2” at 100% maximum dry density, and a CBR at 84% at a Penetration of 0,2” at 95% maximum dry density. Finally, it is worth mentioning that the potential use of this material increases significantly compared to the standard sample, demonstrating physical and mechanical improvements
Downloads
References
J. S., Tingle, y S. R. Jersey, “Evaluation of In Situ Pavement Layers with the Dynamic Cone Penetrometer (DCP)” Environmental Engineering and Science, V 6, 2007
G. Laura, “Estabilización de subrasante con fibra de carrizo en la Av. Independencia, distrito de Ilo”, Concytec, Consejo Nacional de Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación, Perú, 2020
MTC, “Manual de Carreteras Suelos Geológicos, Geotecnia y Pavimentos”, https://portal.mtc.gob.pe/transportes/caminos/normas_carreteras/MTC%20NORMAS/ARCH_PDF/MAN_7%20SGGP-2014.pdf, Ministerio de Transporte y Comunicaciones, 2014
ASTM C143, “Standard Test Method for Slump of Hydraulic Cement Concrete”, American Society for Testing and Materials, USA, 2015
C. M. Chavarry Vallejos, R. A. Figueroa Merino y R. E. Reynaga Tejad, “Estabilización química de capas granulares con cloruro de calcio para vías no pavimentadas”, Pol. Con., V 5, N46, DOI: 10.23857/pc.v5i6.1465, 2020
ISO 868:2003, “Plásticos y ebonita - Determinación de la dureza por penetración con punta cónica (dureza de Shore)”, Ginebra: Organización Internacional de Normalización, 2003
ASTM D1037-12, “Standard Test Methods for Evaluating Properties of Wood-Base Fiber and Particle Panel Materials”, West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM International, 2012
ASTM C192/C192M-21, “Standard Practice for Making and Curing Concrete Test Specimens in the Laboratory”, West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM International, 2021
ISO 12439:2010, “Morteros y concretos frescos - Determinación de la densidad”, Ginebra: Organización Internacional de Normalización, 2010
ASTM C39/C39M-21, “Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens” West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM International, 2021
ASTM C143/C143M-20, “Standard Test Method for Slump of Hydraulic-Cement Concrete” West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM International, 2020
ISO 6782:1982, “Construcción - Construcción de carreteras - Determinación de la densidad y contenido de agua de suelos y materiales tratados con ligantes hidráulicos - Método de prueba nuclear (rápido)”, Ginebra: Organización Internacional de Normalización, 1982
ISO 6781:2007, “Desempeño térmico de edificios - Detección de defectos térmicos en envolventes de edificios - Método de inspección por termografía infrarroja”, Ginebra: Organización Internacional de Normalización, 2007
ASTM C642-21, “Standard Test Method for Density, Absorption, and Voids in Hardened Concrete”, West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM International, 2021
ASTM C39/C39M-21, “Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens. West Conshohocken”, PA: ASTM International, 2021
ASTM C39/C39M-21, “Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens” West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM International, 2021
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The opinions expressed by the authors do not necessarily reflect the position of the editor of the publication or UCLA. The total or partial reproduction of the texts published here is authorized, provided that the complete source and electronic address of this journal is cited. Authors have the right to use their articles for any purpose as long as it is done nonprofit. The authors can post on the internet or any other media the final approved version of their work.






.png)




